Razlika između verzija stranice "Ležaj"
| [nepregledana izmjena] | [nepregledana izmjena] |
m r2.7.1) (robot dodaje: am:ኩችኔታ |
|||
| Red 38: | Red 38: | ||
The maximum speeds that rotational bearings can support also vary, generally performance is defined in terms of the product 'DN' where D is the diameter (often in mm) of the bearing and N is the rotation rate in revolutions per minute. |
The maximum speeds that rotational bearings can support also vary, generally performance is defined in terms of the product 'DN' where D is the diameter (often in mm) of the bearing and N is the rotation rate in revolutions per minute. |
||
== Historija i razvoj == |
|||
An early type of linear bearing was an arrangement of tree trunks laid down under sleds. This technology may date as far back as the construction of the [[Pyramids of Giza]], though there is no definitive evidence. Modern linear bearings use a similar principle, sometimes with balls in place of rollers. |
|||
The first plain and rolling-element bearings were [[wood]], but [[ceramic]], [[sapphire]] or [[glass]] can be used, and [[steel]], [[bronze]], other metals, and plastic (e.g., [[nylon]], [[polyoxymethylene]], [[teflon]], and [[UHMWPE]]) are all common today. Indeed, stone was even used in various forms. Think of the "jeweled pocket watch", which incorporated stones to reduce frictional loads, and allow a smoother running watch. Of course, with older, mechanical timepieces, the smoother the operating properties, then the higher the accuracy and value. Wooden bearings can still be seen today in old water mills where the water has implications for cooling and lubrication. |
|||
Rotary bearings are required for many applications, from heavy-duty use in vehicle axles and machine shafts, to precision clock parts. The simplest rotary bearing is the '''sleeve bearing''', which is just a cylinder inserted between the wheel and its axle. This was followed by the '''roller bearing''', in which the sleeve was replaced by a number of cylindrical rollers. Each roller behaves as an individual [[wheel]]. The first practical caged-roller bearing was invented in the mid-1740s by [[horology|horologist]] [[John Harrison]] for his H3 marine timekeeper. This used the bearing for a very limited oscillating motion but Harrison also used a similar bearing in a truly rotary application in a contemporaneous regulator clock. |
|||
An early example of a wooden ball bearing (see [[rolling-element bearing]]), supporting a rotating table, was retrieved from the remains of the [[Roman Republic|Roman]] [[Nemi ships]] in [[Lake Nemi]], [[Italy]]. The wrecks were dated to [[40 AD]]. [[Leonardo da Vinci]] is said to have described a type of ball bearing around the year [[1500]]. One of the issues with ball bearings is that they can rub against each other, causing additional friction, but this can be prevented by enclosing the balls in a cage. The captured, or caged, ball bearing was originally described by [[Galileo Galilei|Galileo]] in the [[1600]]s. The mounting of bearings into a set was not accomplished for many years after that. The first patent for a ball race was by [[Philip Vaughan]] of [[Carmarthen]] in [[1794]]. |
|||
[[Friedrich Fischer]]'s idea from the year 1883 for milling and grinding balls of equal size and exact roundness by means of a suitable production machine formed the foundation for creation of an independent bearing industry. |
|||
[[Datoteka:Tapered steering head bearings.jpg|thumb|Tapered steering head bearings for a [[motorcycle]]]] |
|||
The modern, self-aligning design of ball bearing is attributed to [[Sven Wingquist]] of the [[SKF]] ball-bearing manufacturer in [[1907]]. |
|||
[[Henry Timken]], a 19th century visionary and innovator in carriage manufacturing, patented the tapered roller bearing, in 1898. The following year, he formed a company to produce his innovation. Through a century, the company grew to make bearings of all types, specialty steel and an array of related products and services. |
|||
[[The Timken Company]] (Sale $4,973.4M, 2006), The [[SKF]] company($6,195.1M, 2005), the [[Schaeffler Group]] (Private), the [[NSK]] company($5,344.5M, 2006), and the [[NTN]] Bearing company($3,697.8M, 2006) are now the largest bearing manufacturers in the world. |
|||
== Također pogledajte == |
== Također pogledajte == |
||
Verzija na dan 18 april 2011 u 18:25
Ovaj članak nije preveden ili je djelimično preveden. |
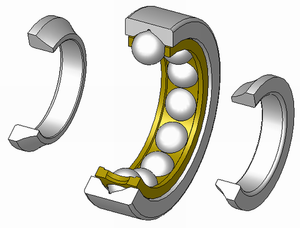
Ležaj je mehanička sprava koja dozvoljava određeno relativno kretanje između dva dijela, najčešće rotaciju ili linearno pomijeranje. Ležaji se mogu klasifikovati prema kretanjima koja dozvoljavaju, prema principu njihovog funkcionisanja, te prema pravcu primjenjene sile, koju oni primaju.
Trenje u ležajevima
Ležajevi sa malim trenjem često su bitni za efikasnost, kako bi se smanjilo habanje, te kako bi se dostigle velike brzine. U suštini, ležaj može smanjiti trenje pomoću svog posebnog oblika, materijala, ili pomoću fluida koji se nalazi između površina.
- pomoću oblika, dobija prednost korištenjem sferičnih površina ili kotrljajnih tijela.
- pomoću materijala, gdje se iskorištava priroda materijala od kojeg je izrađen ležaj. (Na primjer, korištenje plastike za ležaje koji imaju mali koeficijent trenja.)
- pomoću fluida, iskorištava se niska viskoznost sloja fluida, kao što je lubrikant ili kao potišteni medij koji priječava da se dva čvrsta dijela dodiruju.
- pomoću polja, iskorištava elekomagnetna polja, kao što je magnetno polje, kako bi se priječilo dodirivanja dva čvrsta dijela.
Kombinacije se mogu primijeniti čak u istom ležaju. Primjer ovoga je kada se od plastike izradi kavez ležaja, koji odvaja valjkiće/kuglice, koje smanjuju trebhe pomoću svog oblika i završne obrade površine.
Glavni tipovi
Common motions include linear/axial and rotary/radial. A linear bearing allows motion along a straight line, for example a drawer being pulled out and pushed in. A rotary bearing or thrust bearing allows motion about a center, such as a wheel on an axle or a spindle through a housing. Common kinds of rotary motion include both one-direction rotation and oscillation where the motion only goes through part of a revolution, such as with a hinge. Other kinds of bearings include spherical bearings such as ball joints which are used in car suspensions and some computer mice.
Principi funkcionisanja
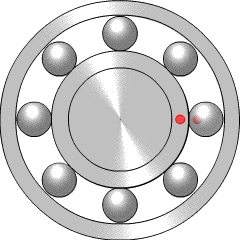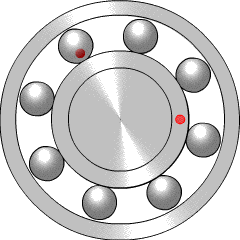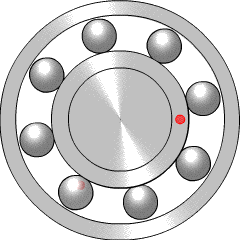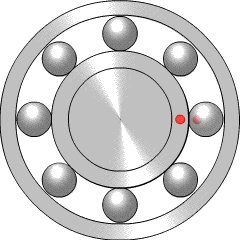
Postoji najmanje šest principa rada ležaja:
- klizni ležaj
- ležaj sa kotrljajućim tijelom, kao što su kugličasti ležaji
- dijamantni ležaj
- fluidni ležaj, kod kojeg se teret drži gasom ili tekućinom
- magnetni ležaj, kod kojeg se teret drži magnetnim poljem
- savojni ležaj
Nošenje opterećenja i performanse ležaja
Bearings vary greatly over the forces and speeds that they can support.
Forces can be radial, axial (thrust bearings) or moments perpendicular to the main axis.
The maximum speeds that rotational bearings can support also vary, generally performance is defined in terms of the product 'DN' where D is the diameter (often in mm) of the bearing and N is the rotation rate in revolutions per minute.
Također pogledajte
- Kuglični ležaj
- Kuglični žlijeb
- Kombinovani ležaj
- Fluidni ležaj
- Hertzov kontaktni napon
- Glavni ležaj
- Ležaj sa igličastim kotrljajnim tijelom
- Rolamit
Vanjski linkovi
- Uopsteno o lezajima - Vrste i tipovi lezaja
- How Bearings Work - Animations and functioning
- How Bearings Work - - Animacije na www.mechanismen.be
- Rano otkrivanje kvara ležaja - studija
